The Ultimate HVAC Guide for Texas Homeowners
Is your HVAC system a mystery to you? You’re not alone. Many homeowners find their Heating, Ventilating, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems to be complex and somewhat enigmatic. However, gaining an understanding of how your HVAC system operates can significantly enhance your ability to maintain it efficiently, leading to savings on energy costs and avoiding expensive repairs.
This guide aims to demystify your home’s HVAC system, breaking down its key components and their functions. We’ll also share essential maintenance tips and insights on making smart choices for system repairs or replacements. Whether you’re navigating home ownership for the first time or looking to deepen your HVAC knowledge, this guide empowers you to optimize your home comfort throughout the year.
Your HVAC System's Core Components
A well-functioning HVAC system is central to your home’s comfort, adjusting temperatures and ensuring clean indoor air quality. Let’s dive into the primary components that keep your system running:
The Furnace: Acting as the powerhouse of your HVAC system, the furnace heats your home using fuel sources like gas, oil, or electricity, distributing warm air to various spaces.
Air Conditioner: Your AC unit works to cool your home, extracting indoor heat and releasing it outdoors, thanks to critical parts like the compressor and evaporator coil.
Ductwork: This network of tubes delivers heated or cooled air from your furnace or AC to rooms throughout your house, playing a vital role in maintaining even temperatures.
Thermostat: This device acts as your HVAC system’s control center, allowing you to set your desired indoor temperature and regulate system operation to maintain it.
Ventilation System: It’s responsible for exchanging indoor air with fresh outdoor air, crucial for maintaining healthy indoor air quality and comfort.
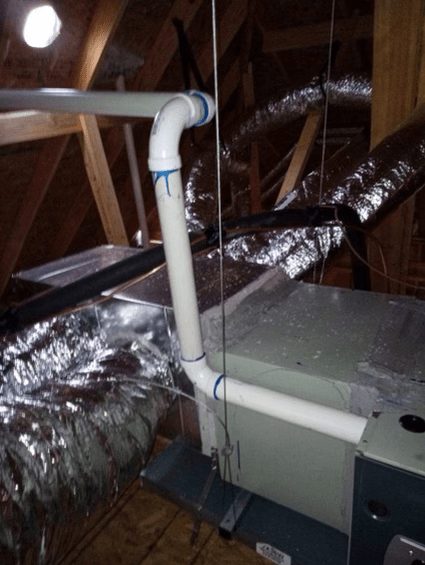

Your Home Heating System
Heat Source: The most crucial component of a heating system is the heat source. This is usually a furnace or boiler that burns fuel (natural gas, oil, propane) or uses electricity to generate heat. In a furnace, air is heated directly; in a boiler, water is heated and either circulated as steam through radiators or as hot water through radiant floor systems or baseboard radiators.
Heat Distribution System: Once the air (in a furnace system) or water (in a boiler system) is heated, it needs to be distributed throughout the home.
- Forced-Air Systems: Utilize a series of ducts to circulate heated air, propelled by a blower motor, throughout the home via air registers or grilles.
- Hydronic Systems (Boilers): Circulate hot water or steam through pipes to radiators, baseboard heaters, or underfloor piping for radiant heat.
Thermostat: Acts as the control center for the heating system, allowing users to set the desired temperature. The thermostat signals the heat source to turn on or off to maintain the set temperature.
How the Heating Process Works
Activation: The process begins when the indoor temperature drops below the setting on the thermostat, signaling the need for heat.
Heat Generation:
- In a Furnace: The burner ignites the fuel (gas, oil, or propane), generating heat in the heat exchanger. A blower fan then pushes air over the heat exchanger to warm it before it’s circulated through the ductwork into the home.
- In a Boiler: Water is heated to boiling, creating steam or hot water. This is then pumped through pipes to radiators or underfloor heating circuits where it releases heat into the rooms.
Distribution: Warm air (from a furnace) or hot water/steam (from a boiler) travels through the home’s ductwork or pipes to various rooms, raising the indoor temperature to the desired level.
Regulation: As the room temperature reaches the set point on the thermostat, the heat source is signaled to shut off until the temperature drops again, maintaining a consistent indoor climate.
Exhaust: Combustion gases produced by the burning fuel are safely vented outside through a flue or chimney in the case of gas or oil systems. Electric furnaces, which do not burn fuel, do not produce these gases and thus do not require venting.
Maintenance and Efficiency
To ensure the heating system operates efficiently and safely, regular maintenance is essential. This includes tasks such as changing air filters in forced-air systems, checking the condition and pressure of water in boiler systems, and professional inspections of the entire system to check for any wear or potential issues.
Your Home AC System
An air conditioning (AC) system works to remove heat and humidity from the interior of a building, improving the comfort of occupants. Here’s a simplified overview of how most residential air conditioning systems, specifically central AC systems, function:
Basic Components of an AC System
Compressor: Located in the outdoor unit, the compressor is responsible for pumping refrigerant throughout the system. It compresses the refrigerant, raising its temperature and pressure.
Condenser Coil: Also located in the outdoor unit, the condenser coil releases the heat carried by the refrigerant into the outdoor air. As the refrigerant cools, it condenses from a gas back into a liquid form.
Expansion Valve: Positioned between the condenser and the evaporator coil, the expansion valve controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. It reduces the pressure of the refrigerant, allowing it to expand and cool before entering the evaporator coil.
Evaporator Coil: Located in the indoor unit, the evaporator coil allows the refrigerant to absorb heat from the indoor air, cooling it. The refrigerant evaporates to a gas as it absorbs heat.
Air Handler and Blower: The air handler circulates indoor air across the evaporator coil for cooling, while the blower fan moves the cooled air into the home’s ductwork, distributing it throughout the rooms.
Thermostat: This is the control system for the AC, allowing users to set their desired temperature. The thermostat signals the air conditioning system to start when the indoor temperature exceeds the set point.
How the AC System Works
Cycle Initiation: The process starts when the indoor air temperature exceeds the temperature setting on the thermostat, signaling the AC system to begin cooling.
Refrigerant Circulation: The compressor pumps the refrigerant to the condenser coil, where it releases its heat to the outdoor air, cooling down and condensing into a liquid.
Cooling the Air: The cooled, liquid refrigerant moves to the evaporator coil via the expansion valve, which decreases its pressure, causing it to cool further. As indoor air is circulated over the cold evaporator coil by the air handler, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the air, cooling it down. The blower then pushes this cooled air through the ducts, lowering the indoor temperature.
Repeating the Cycle: The refrigerant, now warmed by absorbing indoor heat, returns to a gaseous state and travels back to the compressor to begin the cycle anew.
Dehumidification: As air passes over the cold evaporator coil, moisture from the air also condenses on the coil, removing humidity from the indoor air, which enhances comfort.
Efficiency and Maintenance
For an AC system to operate efficiently and effectively, regular maintenance is essential. This includes cleaning or replacing air filters, ensuring the condenser and evaporator coils are clean, checking the refrigerant levels, and verifying that the thermostat is functioning correctly. Professional maintenance can help detect potential issues early, extending the life of the system and preventing costly repairs.
Empowering Homeowners for Better HVAC Management
Armed with knowledge about your HVAC system, you’re better equipped to oversee its maintenance and make informed decisions regarding its care and upgrade. Remember, a proactive approach to HVAC maintenance not only ensures optimal performance but also significantly contributes to your home’s overall comfort and air quality.
For those in Burleson seeking expert HVAC services, Superior AC & Heat stands ready to assist. Our team brings years of experience to every heating and cooling challenge, ensuring your home remains a sanctuary of comfort all year round. Reach out to Superior AC & Heat for all your HVAC needs, and let us bring our expertise directly to your doorstep.